AutoCAD Essentials for Engineers and Designers
This foundational course equips learners with the essential skills to use AutoCAD for 2D drafting and technical drawing. Through guided exercises and real-world design scenarios, students will develop the confidence to create professional blueprints, floor plans, and engineering layouts. Emphasis is placed on precision, layers, scaling, annotations, and drawing organization — key skills across the engineering, architecture, and construction sectors.
Introduction to the AutoCAD interface and workspace
Drawing basic geometric shapes and using modification tools
Layer management and line types
Annotation: dimensions, text, and symbols
Object snaps, tracking, and drawing aids
Working with templates and title blocks
Scaling and plotting drawings for print
Managing complex layouts using blocks and groups
Real-world drafting projects (floor plans, schematics)
Exporting and sharing drawings professionally
Students, civil engineers, architects, mechanical designers, and anyone starting out in the field of technical drawing and 2D drafting.
Lectures
13
Duration
13 weeks
Quizzes
5
Assignments
5
We Train Outstanding AutoCAD Drafter
100k+ Jobs • $50k Starting • Money Back Guarantee
13 Live Classes
Join Live Classes Every Week
5 Real Life Projects
Complete AutoCAD Projects Using Industry Used Tools
Weekly Feedback
Receive Weekly Feedback on Your Work
Job-Ready Portfolio
Build a Job-Ready Portfolio During the Program
Certification of Completion
Graduate with a AutoCAD Certificate
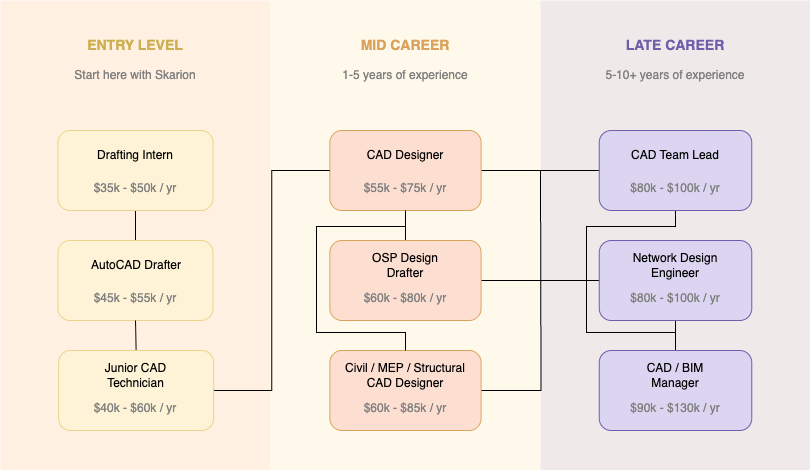
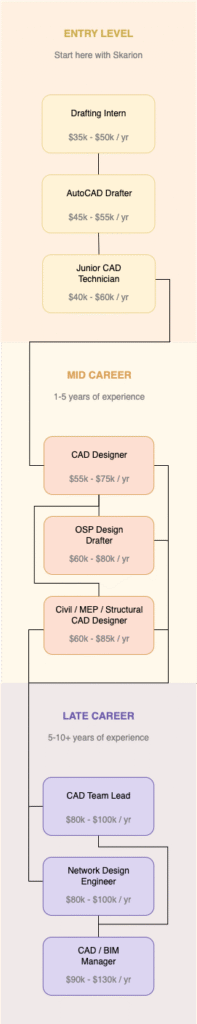
Why is AutoCAD Drafter a Great Career Option?
Longevity • Constant Demand • Flexibility
What Do AutoCAD Drafters Do?
A Day in the Life of an AutoCAD Drafter

Log In and Check Emails
Read project updates, client feedback, and redline markups from the engineering team.
Review Assigned Tasks
Check the drafting schedule or task management system for the day’s deliverables.
Open AutoCAD and Project Files
Load relevant base maps, existing drawings, and client-provided data for the assigned route.
Draft New OSP Fiber Layouts
Begin drawing proposed fiber routes, ducts, handholes, or pole lines based on the design plan.
Coordinate with Design Engineer
Hop on a quick call or chat to clarify specifications, design logic, or field notes.
Finalize Drafting and Layering
Completes the drawing by adding layers, annotations, fiber labels, and legends as per company standards.
QA Review of Completed Drawings
Self-review the drawing for accuracy, layer compliance, and alignment with redlines.
Submit for Internal QC or Supervisor Review
Send the file for quality check or uploads it to the shared folder/project portal.
Work on As-Built or Redline Corrections
Apply markups from completed construction work to convert design into as-built documents.
Update Drawing Logs and Notes
Log work completed, note pending clarifications, and update internal tracking sheets.
End-of-Day Wrap Up
Save all work, sync files to cloud/server, and sign off for the day.
Course Outline
13 Weeks • 13 Live Classes
Week 1: Getting Started with AutoCAD
Introduction to the interface, workspace setup, and drafting environment basics.
Week 2: Drawing Basic 2D Shapes
Learn to draw lines, circles, rectangles, and other fundamental shapes.
Week 3: Editing and Modifying Drawings
Use modify tools like move, trim, offset, and rotate to edit geometry.
Week 4: Mastering Layers and Line Types
Organize drawings with layers, colors, lineweights, and linetypes.
Week 5: Object Snaps and Drawing Aids
Improve accuracy using snaps, tracking, and drawing precision tools.
Week 6: Annotating with Text and Dimensions
Add clear text, dimensions, leaders, and annotation scaling.
Week 7: Creating and Using Blocks
Design reusable components using blocks, attributes, and groups.
Week 8: Working with Templates and Title Blocks
Set up templates and professional title blocks for consistency.
Week 9: Layouts, Viewports, and Scaling
Use paper space layouts, viewports, and proper drawing scales.
Week 10: Plotting and Exporting Drawings
Configure plot settings and export drawings to PDF or print.
Week 11: Project: Drafting a Floor or Site Plan
Apply learned skills to draft a real-world architectural/civil layout.
Week 12: Project: Technical or Fiber Optic Drawing
Create a schematic or fiber layout using blocks and annotations.
Week 13: Final Review and Presentation
Present final project, receive feedback, and explore career applications.
The Skarion Advantage
We Help People Kickstart Their Careers
Job Guarantee
We don’t win unless you do
Mentorship
Real guidance from real experts
Flexible Learning
Learn anytime, from anywhere
How it Works
The quickest and most affordable way to start a career. No experience or degree required!
Consultation
Begin with a Personalized Assessment
Share your background and goals. We’ll help you identify the most suitable career path and training program based on your current skills and aspirations.
Join an Industry Aligned Bootcamp
Enroll in our hands-on, mentor-led programs designed to equip you with practical, job ready skills in high demand fields such as OSP Design and Telecom.
Enroll & Learn
Build Experience
Develop a Portfolio Through Simulated Projects
Work on guided, real-world simulations that mirror actual job tasks. These projects serve as credible experience for your resume and interviews.
Receive Comprehensive Job Placement Assistance
We support your job search with resume building, interview preparation, and active job applications including submitting on your behalf.